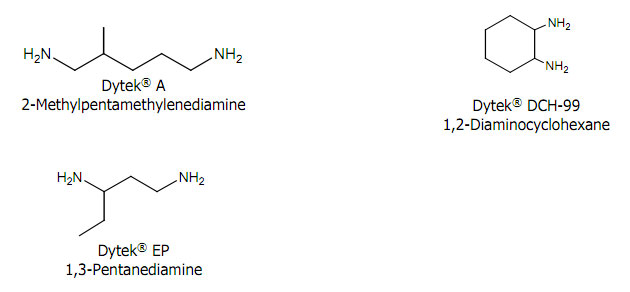
Epoxy resins cured with Dytek® amines have excellent properties for use in coating, civil engineering, adhesive, and composite applications. These properties include greater flexibility for Dytek® A, better chemical resistance and extremely low odor and low color for Dytek® EP, best chemical resistance and higher glass transition temperature for Dytek® DCH-99, and a lower adduct viscosity for Dytek® A, Dytek® EP, and Dytek® DCH-99 versus competitive amines.
Three series of tests, summarized in Tables 1–3,were done for each of the amines to measure their performance with a standard epoxy resin and with two basic epoxy formulations.
Isophoronediamine (IPDA) was included in the test series for comparative purposes.
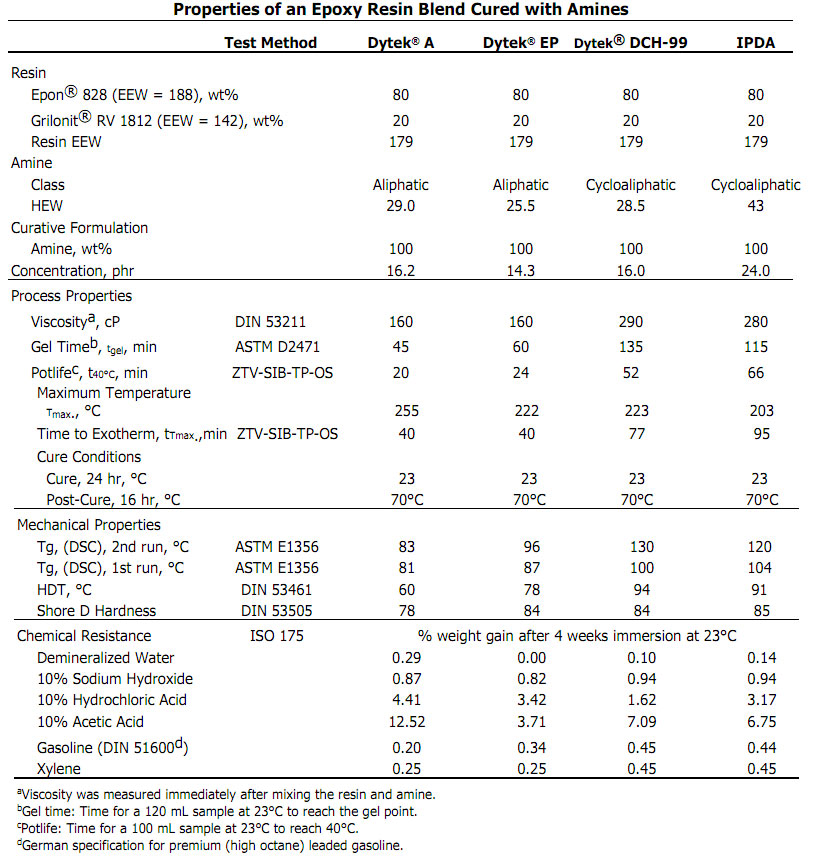
Stoichiometric amounts of each amine were used to cure the resin in all three series. A 24-hr cure at 23°C followed by a 16-hr post-cure at 70°C was used for all formulations. The stoichiometry and cure schedule used may not be optimal in each case. For example, the Dytek® EP, Dytek® DCH-99, and IPDA formulations reported in Tables 1 and 2 were not completely cured using the test cure schedule.
Table 1 summarizes the process properties, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance of Epon® 828 resin cured with Dytek® A and Dytek® EP diamines and with Dytek® DCH-99 and IPDA.
Table 2 summarizes the properties of an Epon® 828 and Grilonit® RV 1812 (hexanediol diglycidylether) resin blend cured with the same diamines.
Table 3 summarizes the properties of the same resin blend cured with four amine adducts.
These adducts were prepared by reacting each diamine with Epon® 828 resin in benzyl alcohol using a 5:1 molar ratio of diamine to resin.
These amine adducts have low viscosities.
Higher levels of adduction, 4:1 molar ratio of diamine to resin, are recommended to optimize surface properties.
The DIN test methods used are listed at the bottom of page 5 along with reference to similar ASTM methods